C175 - Data Management Foundations
Last updated: May 4th, 2023
Intro
DBMS
- Functions:
- Data Dictionary Management
- Data Abstraction and dependence removals
- Data Storage Management
- Performance Tuning
- Data Transformation and Presentation
- Security Management
- UAC
- Integrity Managemnt
- Backup and Recovery Management
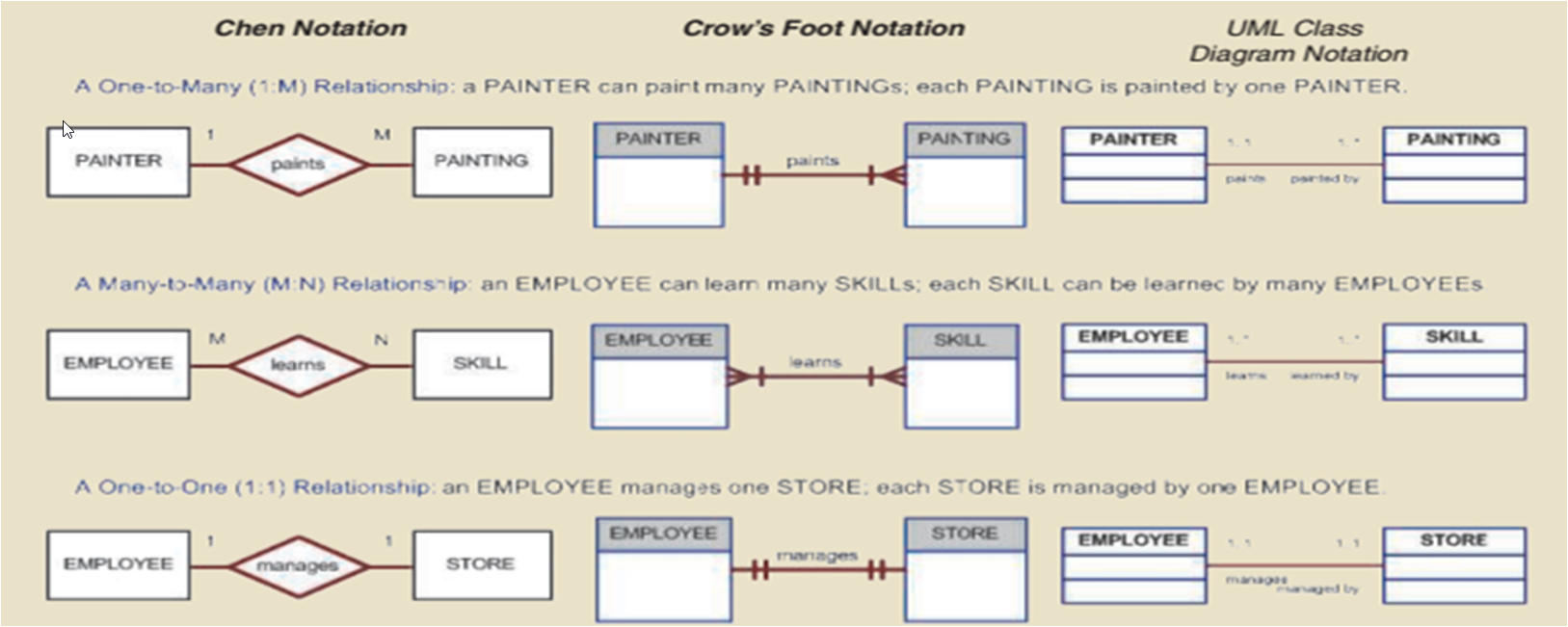
Entity Relationship Diagrams and Data Modelling
Evolution of Data Models
- Hierarchical
- Contains levels, parents and segments(children)
- 1:M
- Network
- Allows a record to have more than one parent
- Relational
- Uses relation tables, tuples and attributes
- ERDs
- Graphical representations of entities and their relationships
- OOM
- Objects, attributes, classes, methods
- Big Data
- 3 Vs
- NoSQL
- Not Only SQL
- Relational vs Cassandra
- Relational:
- Data is stored in a database/schema which contains at least one table
- Tables can be joined
- Cassandra:
- Data is stored in a keyspace which contain column families
- Join is not supported
- Rows are not required to contain same number of columns
- No foreign keys
Crows Foot Notation with Modality
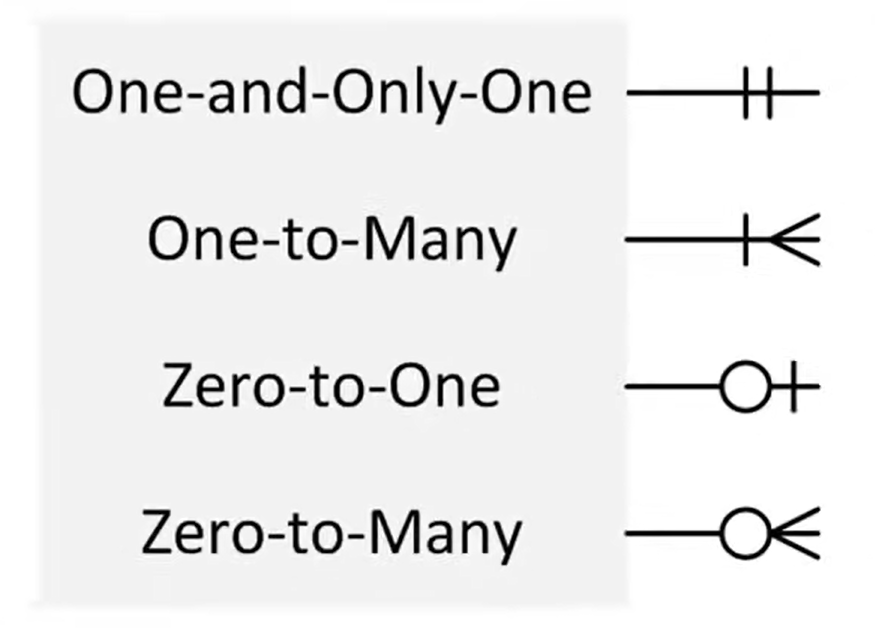
- The minimum will always be on the inside and the maximum on the outside.
- A zero would indicate an optional relationship
Describing Relationships
- Unary
- Relationship with itself
- Binary
- Relationship between two entities
- Ternary
- Relationship between at least three entities.
- 1:1 or 1..1 (One to One)
- A single record has a relationship with a single record in another table
- 1:M or 1..* (One to Many)
- One record in a table is related to more than one record in another
- M:N or *..* (Many to Many)
- A record can be related to one or more records in another table and vice versa.
SQL
DDL: Data Definintion Language
- Define and manage DB structures
- Main SQL commands:
- CREATE
- Create DB objects
- CREATE TABLE Employee(empId Integer NOT NULL, empName Char(25) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT empPk PRIMARY KEY(empID));
- ALTER
- Modify structure of existing DB objects
- ALTER TABLE Employee ADD CONSTRAINT empPk PRIMARY KEY(empId);
- DROP
- Delete existing objects
DML: Data Manipulation Language
- Define, update and retrieve data
- Main SQL commands for defining and updating:
- INSERT INTO
- Add a new row
- INSERT INTO Employee (empId, salaryCode, lastName) VALUES (62, 11, 'Halpert');
- UPDATE
- Update rows
- UPDATE Employee SET phone = '123-867-5309' WHERE empId = 29;
- DELETE FROM
- Delete rows
- DELETE FROM Employee WHERE empId = 29;
- Main SQL commands for retrieving:
- SELECT
- Queries a table and returns result as a 2D relation table.
- SELECT empName FROM Employee WHERE empId = 29;
- SELECT * FROM Employee;
- * = All Columns
- DISTINCT
- Added to SELECT to suppress duplicates
- SELECT DISTINCT deptId FROM Employee;
- WHERE
- Allows matching
- =
- <> or !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- IN
- SELECT empName FROM Employee WHERE deptId IN (4, 8, 9);
- AND
- Intersection
- OR
- Union
- NOT
- Exclusion
- BETWEEN
- Range
- LIKE
- Allows wildcard search
- %
- Match all
- _
- Match letter
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
- Same functionality as WHERE
- SELECT salespersonId, salespersonLastName, SUM(saleAmount) AS totalSales FROM Sales GROUP BY salespersonId, salespersonLastName HAVING SUM(saleAmount) >= 10000;
- ORDER BY
- ORDER BY empName DESC;
- ORDER BY empName ASC;
- Default
- COUNT, MIN, MAX, SUM, AVG, STDEV
- JOIN
- Combine data from multiple tables
- Outer Join:
- Left Outer Join
- SELECT empName, deptName FROM Employee E LEFT OUTER JOIN Department D ON E.deptId = D.deptId;
- Full Outer Join
- Right Outer Join
- Inner Join:
- Must have matching values from both tables
- Implicit join via WHERE:
- SELECT empName, deptName FROM Employee AS E, Department AS D WHERE E.deptId = D.deptId
- Explicit join:
- SELECT empName, deptName FROM Employee E INNER JOIN Department D ON E.deptId = D.deptId WHERE D.deptName NOT LIKE 'Account%';
DCL: Data Control Language
- Create user accts and manages permissions
Data Modeling
Keys
- Unique
- Primary Key
- Main key that identifies a row in a table
- never changing, never null
- Candidate Key
- Has the potential to become a primary key
- Smallest combination of columns for uniqueness
- Composite Key
- Composed of two or more columns
- Surrogate Key
- Added to a relation to act as the primary key
- Not a natural key
- Non-Unique
- Foreign Key
- A primary key that links multiple tables.
- Referential integrity ensures foreign keys refer to an entity
- DELETE, UPDATE, INSERT
Keys and Relationships
- 1:1
- Optional side will recieve the foreign key
- 1:M
- The Many side recieves the foreign key
- M:M
- The intersection has a composite key
Normalization
- Ensuring that a relation is well formed
- Dependency Concepts
- Functional dependence
- B is fully functionally dependent on A if each value of A determines only one value of B
- Partial Dependency
- Attribute is dependent on a portion of the primary key
- Transitive Dependency
- Attribute is dependent on something other than the primary key
- Normal Forms:
- 1NF
- Cells hold a single value (atomicity)
- 2NF
- 1NF + no partial dependencies
- 3NF
- 2NF + no transitive dependencies
- Boyce-Codd
- Every determinant is a candidate key
Conversion
- To 1NF
- Eliminate repeating groups
- Identify primary keys
- Identify dependencies
- To 2NF
- Make new tables to eliminate partial dependencies
- Reassign corresponding dependent attributes
- To 3NF
- Make new tables to eliminate transitive dependencies
- Reassign corresponding dependent attributes
Business Intelligence
Reporting
- Filter, sort, group, and make simple calc
- Summaries, comparisons, classifications
- Report delivery crucial
- OLAP
- OnLine Analytical Processing
- Used for dynamically examining database data
- Input = dimensions; Output = measures
- Results in OLAP Cube/Report
Data Mining
- Analyze, predict and decision-making
- Uses sophisticated math and stats